With the continuous advancement of LED technology, LED applications have become increasingly popular in the medical and health fields. LEDinside has compiled innovative applications of LEDs in adjuvant therapy and health monitoring in recent years, including smart skin, promoting hair growth, monitoring blood sugar, assisting cancer treatment, monitoring blood oxygen, and more.
Micro LED skin monitoring system
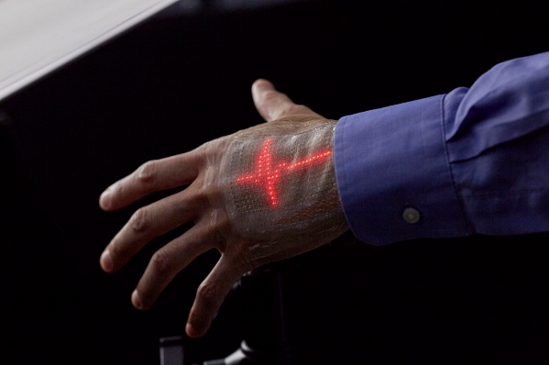
In February 2018, the University of Tokyo and DNP Dai Nippon Printing collaborated to develop a skin-sensitive electronic sensor "skin electronics". This ultra-thin, malleable, flexible monitoring system consists of a flexible screen and a lightweight sensor that uses a permeable nano-electrode and a wireless communication module.
The system records the user's biochemical indicators through sensors and displays relevant information on the screen. These health information can also be shared through the cloud and other devices. This product is designed to help older people or patients who are unfamiliar with medical device operations to record health-related data to help determine physical condition.
According to DNP Dainippon Printing Co., Ltd., the sensing system is expected to enter the market in the next three years. They are currently working to optimize the structure, improve the production process, improve the credibility of product data, and overcome the need to cover large areas of skin. Technical problems.
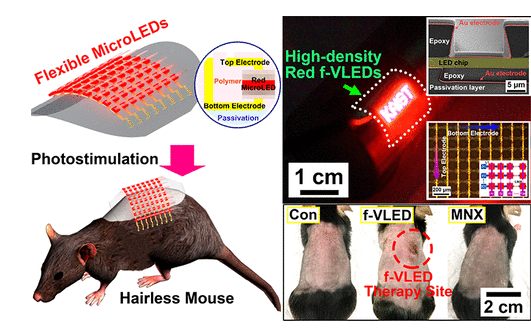
Micro LED wearable device promotes hair growth
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed a Micro LED wearable device that uses vertical Micro LEDs to successfully help mice re-grow their hair.
The device was tested on a back of a mouse that shaved hair using a flexible array of 900 vertical Micro LEDs. After 20 consecutive days of treatment, the hair growth of the mice was significantly faster than that of the untreated mice. Moreover, after treatment, the newly grown hair of the mouse is longer and the hair area is wider.
According to KAIST, Micro LEDs do not heat up to the detriment of the human body and consume only one thousandth of the energy per unit area compared to conventional phototherapy lasers. The research results can provide a new method for the treatment of human hair loss.
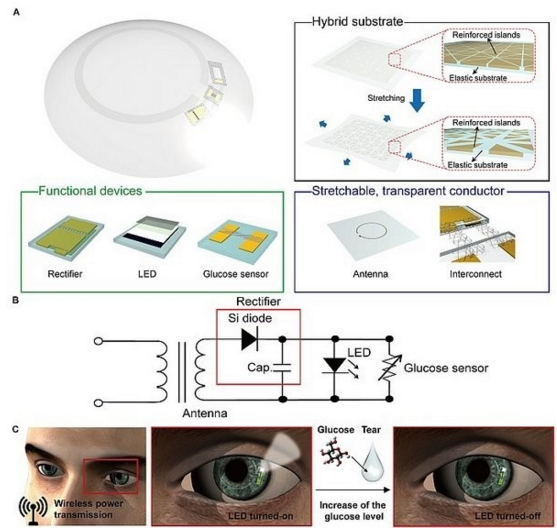
Intelligent contact lenses for measuring blood sugar
The research team at the Ulster Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in Korea has developed a smart contact lens consisting of a blood glucose sensor, a wireless power transmission circuit and LEDs. The contact lens monitors blood glucose levels by monitoring the glucose concentration in the tears of diabetic patients and displays the results in real time through an embedded LED screen.
In addition, imec has partnered with Ghent University and contact lens manufacturer SEED to develop a product that combines LED lights and contact lenses. This product incorporates a transducer into the lens for the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases. They also suggest that contact lenses can be used more widely, such as delivering drugs in eye treatments.
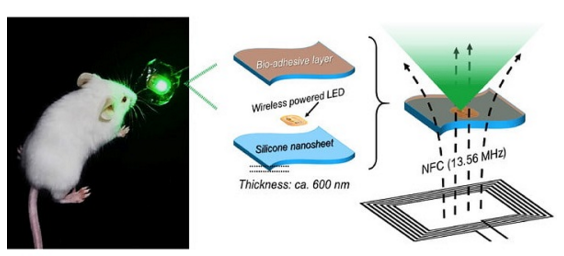
Implantable LED device for cancer treatment
Waseda University in Japan also uses LEDs to treat cancer. It is reported that the research team of the school has developed an LED implantable device, which consists of LED chips and bioadhesive nanosheets to successfully shrink tumors in mice through phototherapy.
The implantable device uses metrological photodynamic therapy for the inner surface of animal tissue and releases low intensity radiation to treat targeted lesions for therapeutic purposes. The therapy is a long-term treatment that uses low-dose special drugs and special lighting to kill cancer cells. By using metrological photodynamic therapy directly at the targeted lesion. Can reduce the impact on healthy areas.